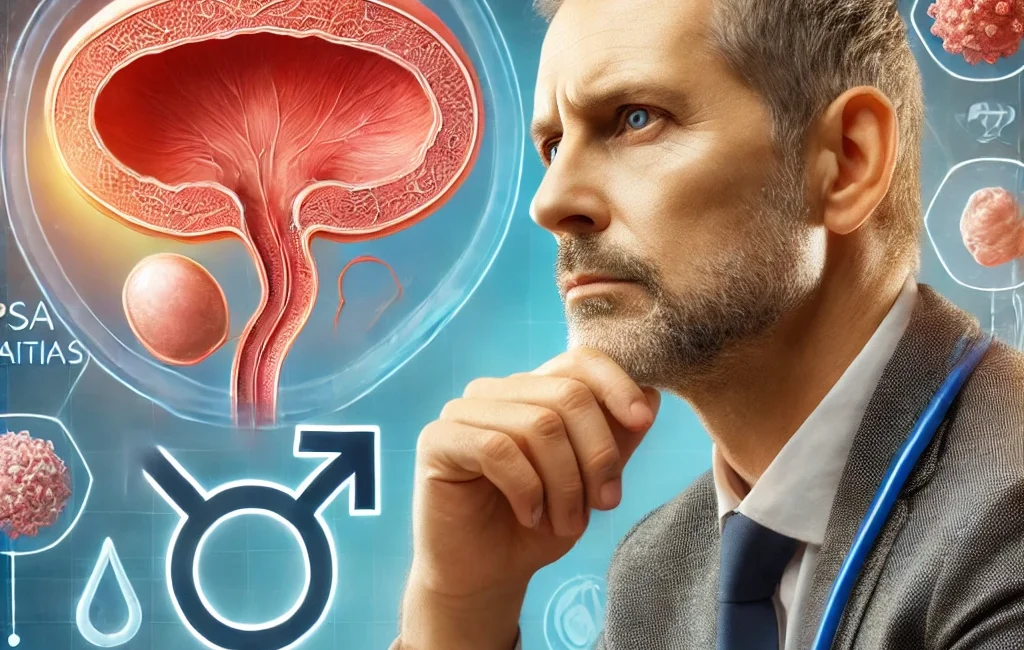
Prostate health is a critical issue for men, particularly as they age. The prostate, a small gland that produces seminal fluid, can become the source of various health problems, including benign enlargement, infections, and prostate cancer. With prostate cancer being one of the most common cancers among men, understanding how to maintain prostate health through prevention, screenings, and treatment options is essential for long-term well-being.
Importance of Prostate Health
Prostate issues are common, especially in older men. Conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate), and prostate cancer can affect the quality of life and overall health. Approximately 1 in 9 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during their lifetime, making early detection and management key to effective treatment and better outcomes.
Prevention Strategies for Prostate Health
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Diet plays a significant role in prostate health. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help protect prostate cells from damage. Tomatoes, in particular, contain lycopene, a potent antioxidant linked to a reduced risk of prostate cancer. Additionally, foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and flaxseeds, can help lower inflammation and promote prostate health.
- Regular Exercise: Staying active can lower the risk of developing prostate conditions. Studies suggest that men who engage in regular physical activity are less likely to experience prostate problems, including cancer. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, which is vital as obesity is a risk factor for prostate cancer.
- Reduce Alcohol and Tobacco Use: Limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking can reduce the risk of prostate-related issues. Smoking, in particular, has been linked to more aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
Screening and Early Detection
Screening is crucial in catching prostate cancer early when it is most treatable. Two primary tests used for prostate screening are:
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: The PSA blood test measures the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. Elevated levels can indicate the presence of prostate cancer or other prostate conditions, such as BPH or prostatitis.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): During a DRE, a doctor checks for abnormalities in the size, shape, or texture of the prostate gland, which could indicate prostate issues, including cancer.
The American Cancer Society recommends that men discuss prostate screening with their doctor starting at age 50, or earlier (age 40-45) if they are at higher risk, such as men with a family history of prostate cancer.
Treatment Options for Prostate Conditions
- Watchful Waiting/Active Surveillance: For men with slow-growing prostate cancer or mild symptoms of BPH, doctors may recommend close monitoring rather than immediate treatment.
- Medications: For conditions like BPH, medications such as alpha-blockers or 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can help reduce symptoms by relaxing the muscles around the prostate or shrinking the gland.
- Surgical Options: In more severe cases of prostate enlargement or cancer, surgery may be necessary. Procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) can alleviate BPH symptoms, while prostatectomy (removal of the prostate) may be required for treating prostate cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is commonly used for treating prostate cancer, especially in the early stages. It targets cancer cells while sparing surrounding healthy tissue.
Conclusion
Prostate health is an essential aspect of men’s overall health, especially as they age. By adopting preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly, men can reduce their risk of prostate issues. Regular screenings, including PSA tests and DREs, are vital for early detection and successful treatment. With various treatment options available, men should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan for maintaining optimal prostate health.